
Get Element at Index : Return the element at specific index, if index is greater than the size then return –1. Get Size: returns the size of the linked list. If size is 0 then make the new node as head and tail else put node at the end of the list using tail reference and make the new node as tail.ĭelete at the Start : Delete a node from beginning of the linked list and make the head points to the 2nd node in the list.

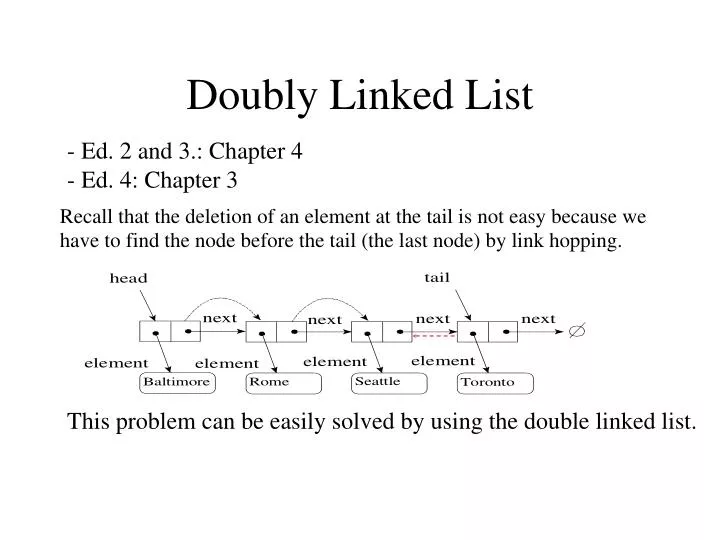
If size is 0 then make the new node as head and tail else put the at the start, change the head and do not change the tail.Īdd at the End : Add a node at the end of the linked list. Furthermore, there are two fields in each node: data and a pointer to the next field. Besides, pointers are used to connect nodes. The linked list is a type of linear data structure that is defined as a collection of nodes. Head points the start of the linked list and tail points to the last node of the linked list.Īdd at the Start : Add a node the beginning of the linked list. What is Java doubly linked list In fact, the Doubly Linked list java is a type of linked list. NOTE: we are two references here, head and tail. Let’s see how the Node structure will look like So as we can see the in doubly linked list each node has two references, next and prev which makes it possible to traverse in both directions. Traverse in both direction, back and froth Singly Linked List vs Doubly Linked List Singly Linked List Let’s see the difference between singly and doubly linked list.
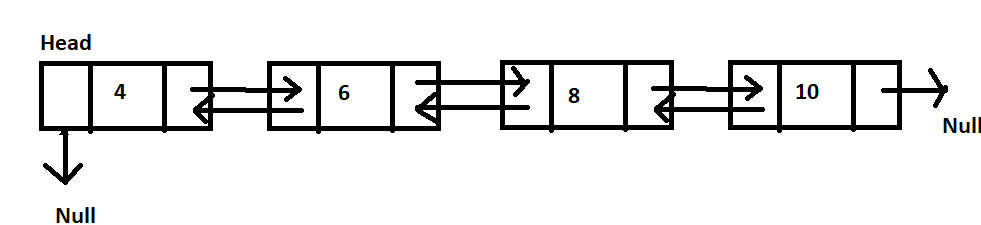
I would suggest that if you do not about Linked list, first read “Singly Linked List” In a way you say that it’s an extension of singly linked list.
Doubly linked list how to#
In this article we will see what is doubly linked list, how it is different from other linked list and how to implement it.Įarlier we have seen what is Singly Linked List and Circular Linked List and How to implement it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
